Ford IDS Software Download FREE Link – Remote Support
The Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic Software) helps technicians diagnose and program Ford and Mazda vehicles quickly and accurately. Need a reliable Ford IDS download? At VCCarTool, we provide everything you need to download, install, and set up Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic Software) for accurate diagnostics and programming on Ford and Mazda vehicles. Follow our expert guide to access the latest Ford IDS version and optimize your vehicle servicing with confidence.

What is Ford IDS software?
Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System) is the official factory diagnostic software designed for use with Ford VCM II, VCM 3, VCM, VCMM Interfaces. IDS provides complete dealer-level vehicle diagnostics for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles. Technicians use IDS to diagnose and service vehicles up to 2018 and forward vehicles.
You can see the full set of software and diagnostic equipment specifically for Ford at: Ford Diagnostic Tool Software
Key Features of Ford IDS
-
Read and Clear Fault Codes (DTCs): Identifies and clears trouble codes from various control modules.
-
Data Logging (DATALOGGER): Live data stream (DataStream) viewing and recording for in-depth diagnostics.
-
Actuator Tests: Activates components (e.g., fuel pump, fan, injectors) to check functionality.
-
ECU Programming: Supports reprogramming and module replacement (e.g., PCM, BCM).
-
Service Functions: Key programming, brake bleeding, throttle relearn, and more.
-
Vehicle Coverage: Supports Ford and Mazda models up to 2018 (in your provided license).
-
License Duration: 1 year.
-
Supported Languages: English, German, French, Italian, Spanish, Swedish, Dutch, Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, Portuguese.
This software provides complete dealer-level diagnostic capabilities, making it the perfect choice for professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Why Is Ford IDS Important?
Ford IDS is essential because it provides full access to the vehicle’s systems, just like an official Ford dealership tool. Unlike generic diagnostic tools, Ford IDS can perform advanced tasks such as module programming, system calibrations, key programming, ECU flashing, and complex diagnostics. Using Ford IDS ensures precise, up-to-date, and manufacturer-approved repairs and configurations, which are critical for maintaining vehicle performance, safety, and reliability.
How to Download and Install Ford IDS?
1. System Requirements for Ford IDS Download
Before downloading and installing the Ford IDS software, ensure your computer meets the minimum system requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 7 (64-bit) or Windows 10 (64-bit)
- Processor: Intel Core i5 or higher
- RAM: Minimum 4GB
- SSD Hard Drive: At least 20GB of free space for installation and smooth operation
Recommended Laptops for Ford Technicians:
- Panasonic Toughbook CF-D1
- Panasonic Toughbook CF-19
- Panasonic Toughbook CF-31
- Panasonic Toughbook CF-53
We recommend Car Diagnostic Laptop here.
2. Step-by-Step Ford IDS Software Download Guide
Follow these detailed steps to download and install Ford IDS software correctly. If you encounter issues during installation, contact us for remote support.
Step 1: Download Ford IDS Software
- Click on the download link above or contact VCCarTool via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927: Click here
- Select the latest version: IDS 130 Full + FDRS 35.5.5
Note: Our article only provides free download links and disclaims responsibility if you make a mistake in downloading. For the best support, please contact our technical team at WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927.
Step 2: Run the Installer as Administrator
- Once downloaded, right-click on IDS_130_Setup.exe and select “Run as Administrator” to start the installation.
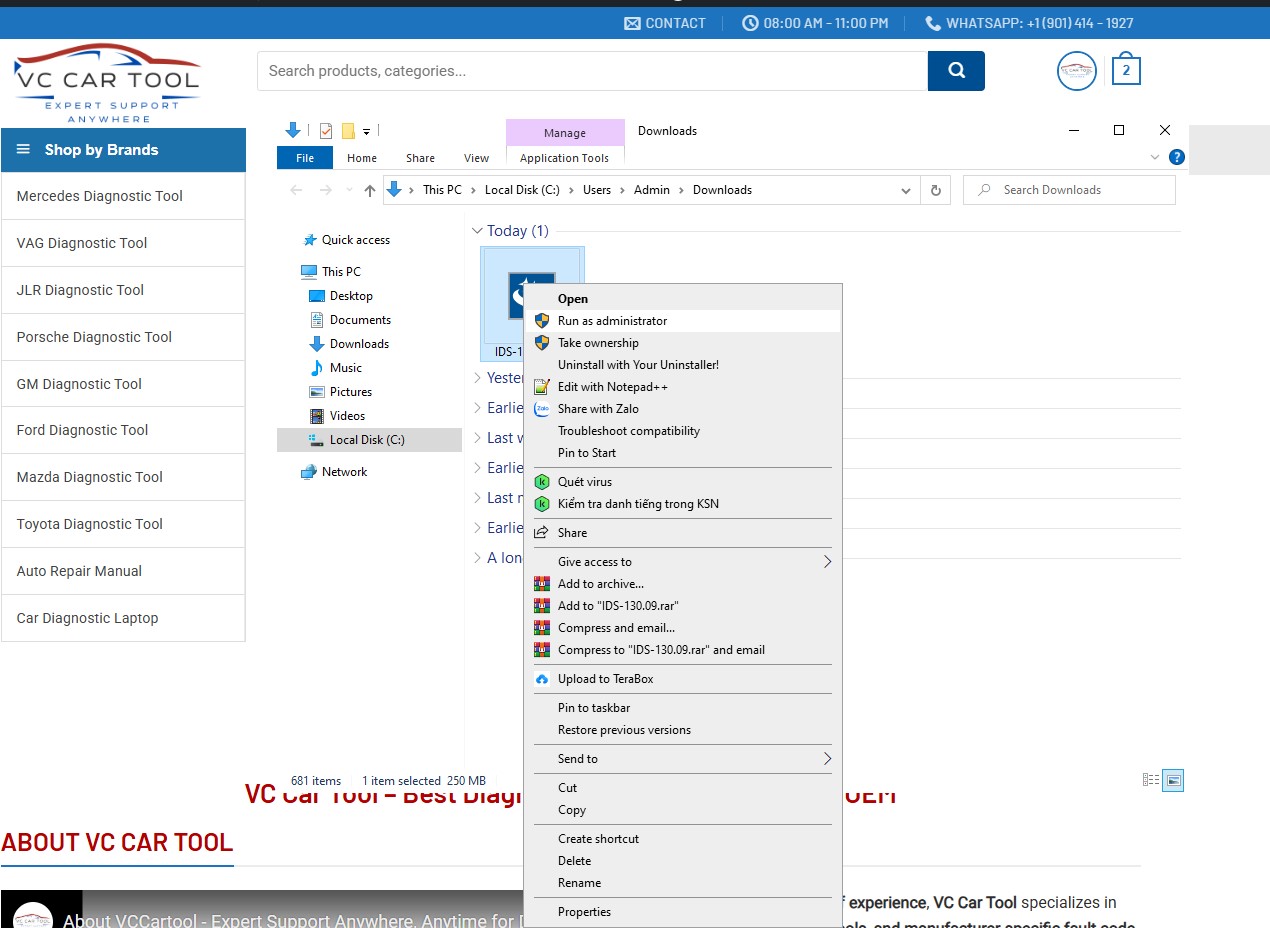
Select “Run as Administrator” to start the installation
Step 3: Initial Ford IDS Configuration
- Select your preferred language and click “Next”
- Accept the license agreement by selecting “I accept the terms of the license agreement”
- Click “Next” to proceed
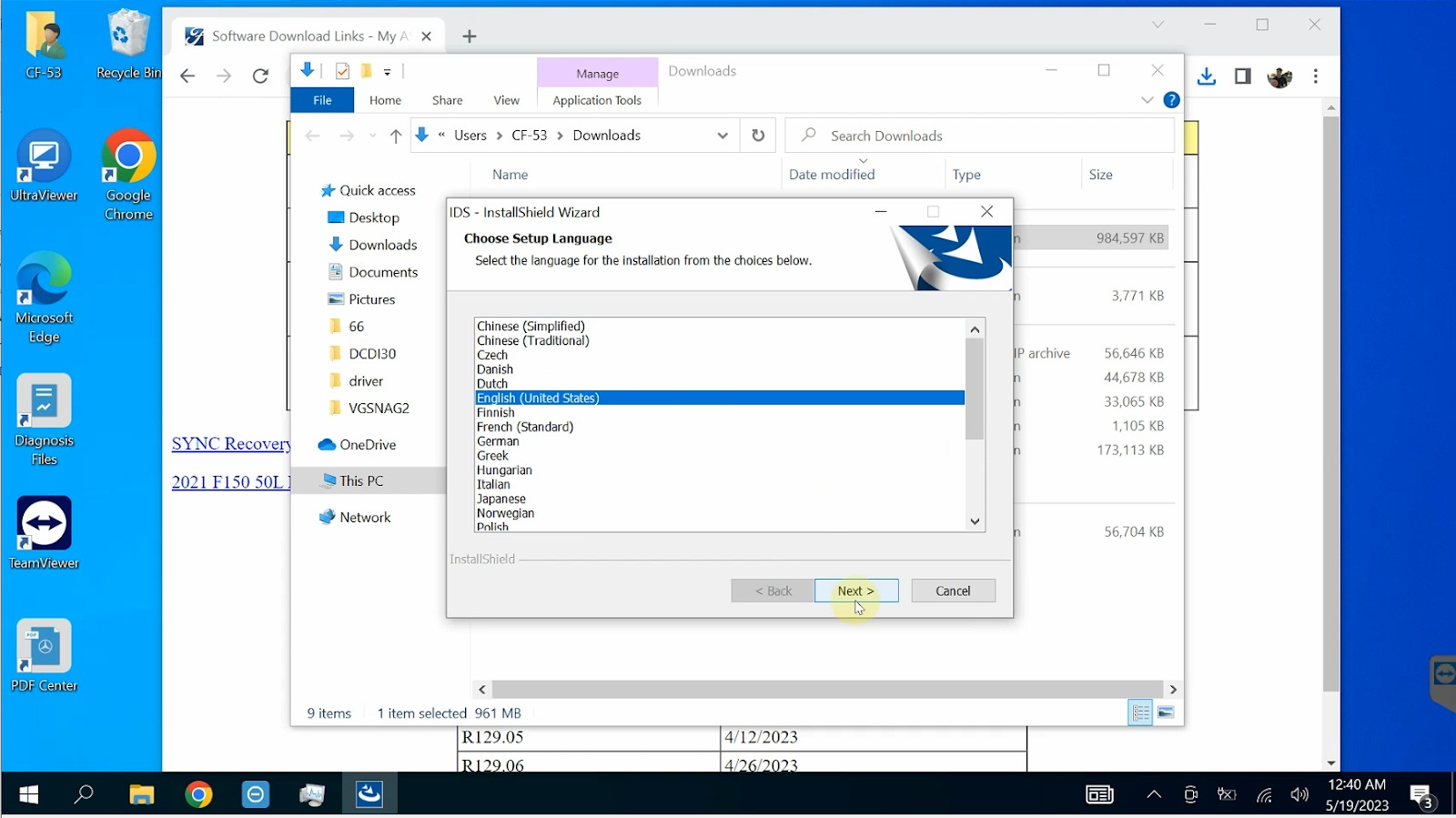
Select language and press “Next”
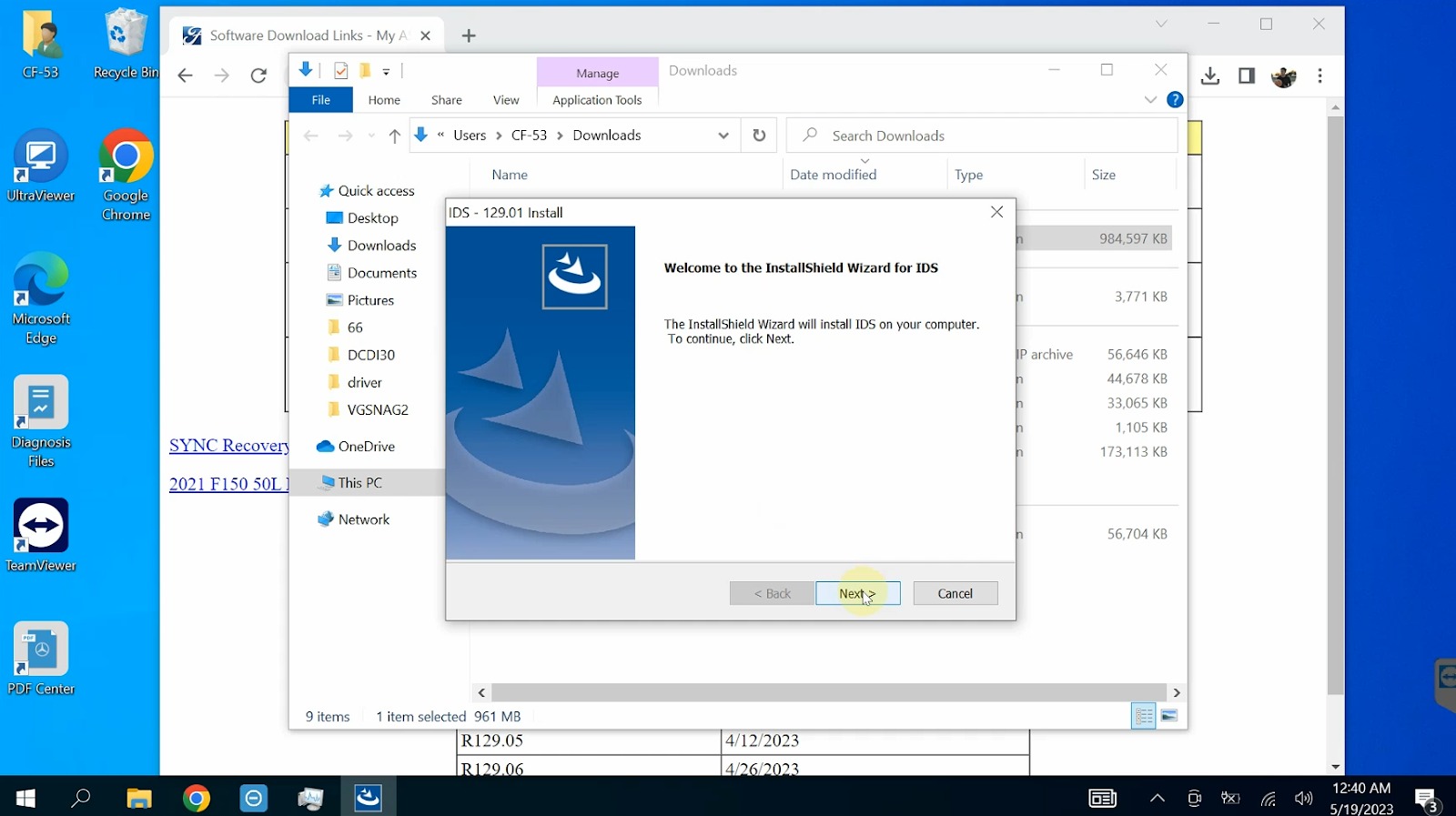
Click “Next”
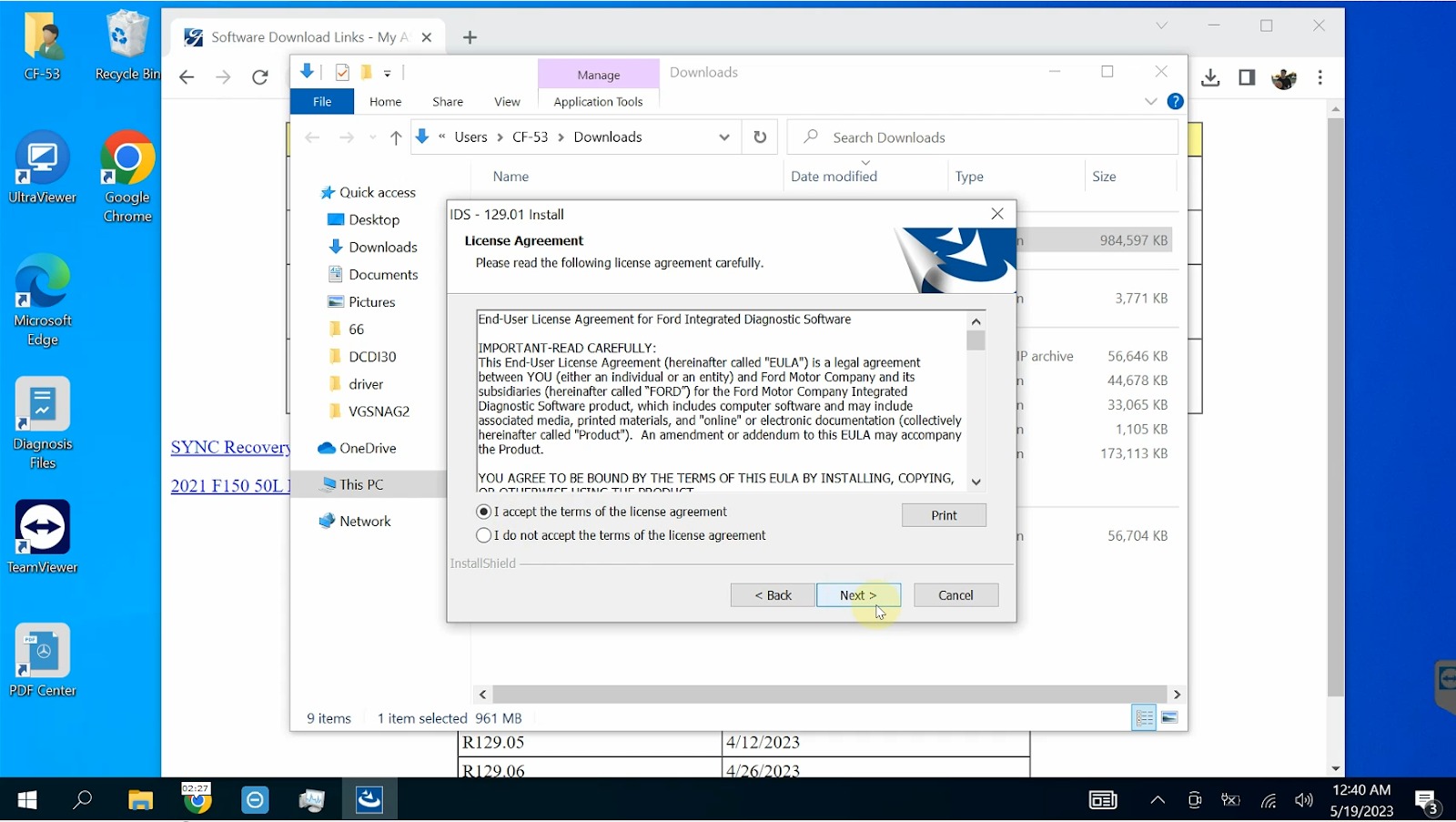
Select “I accept the terms of the license agreement” then press “Next”
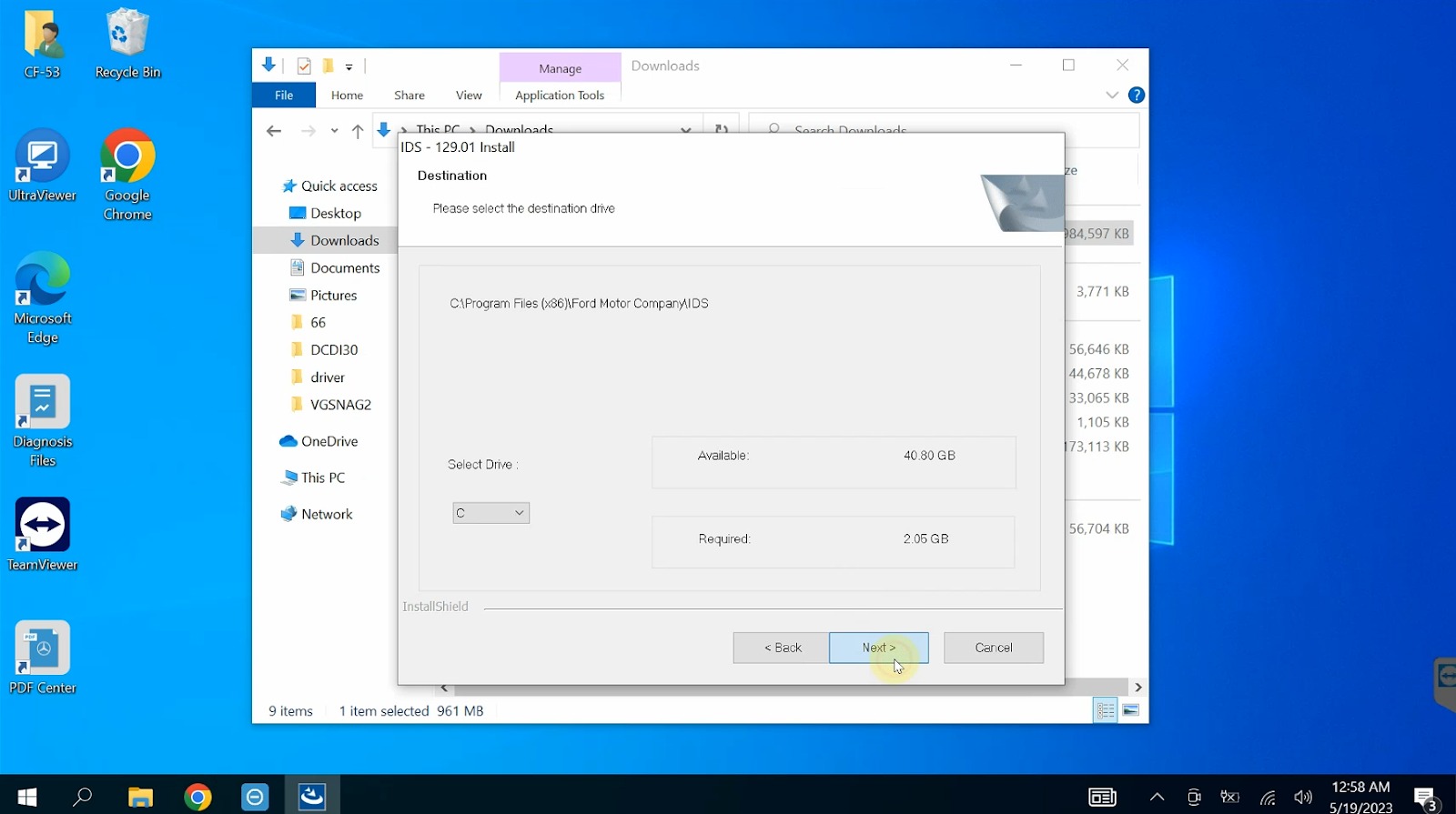
Click Next
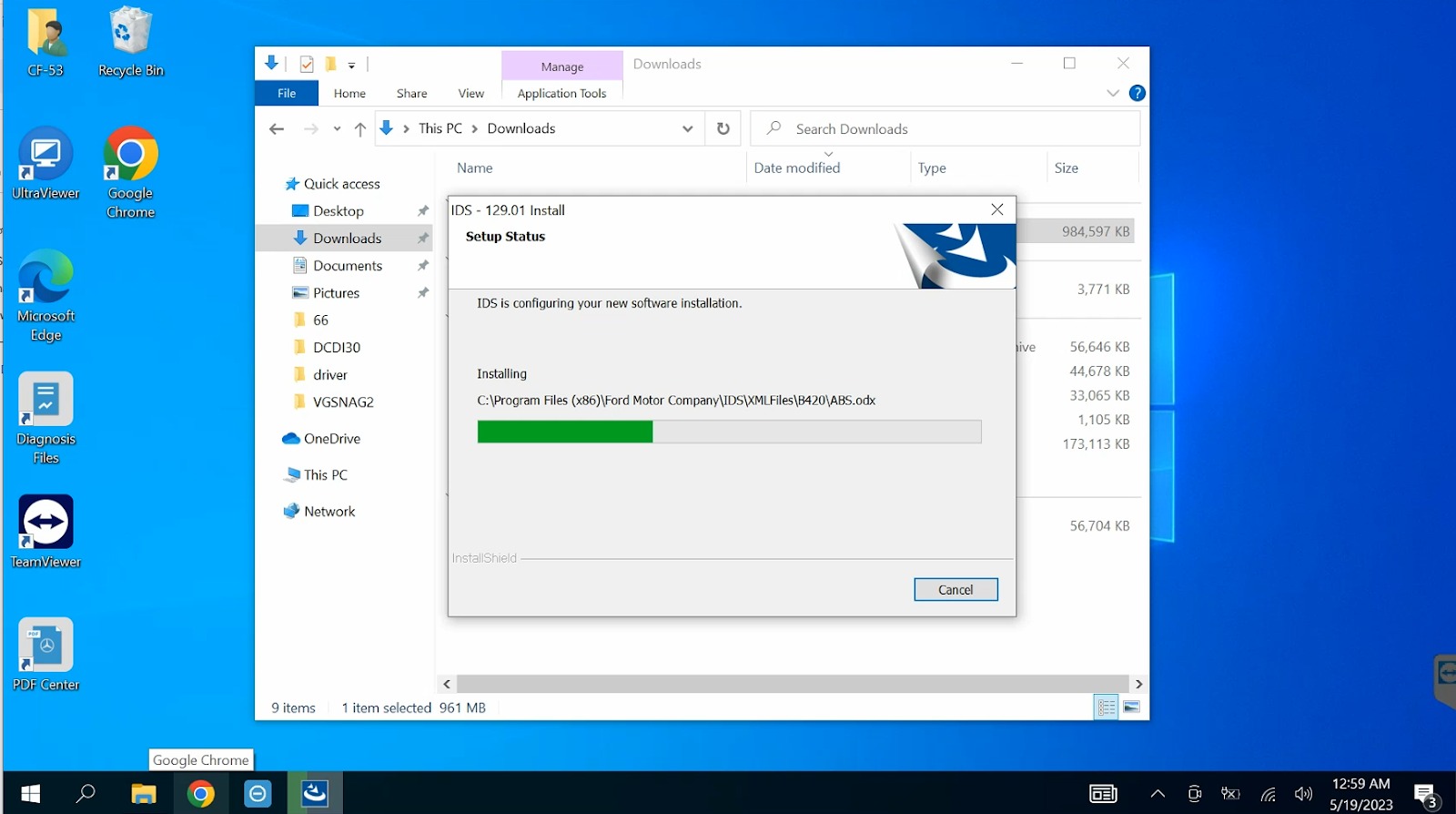
Waiting for download
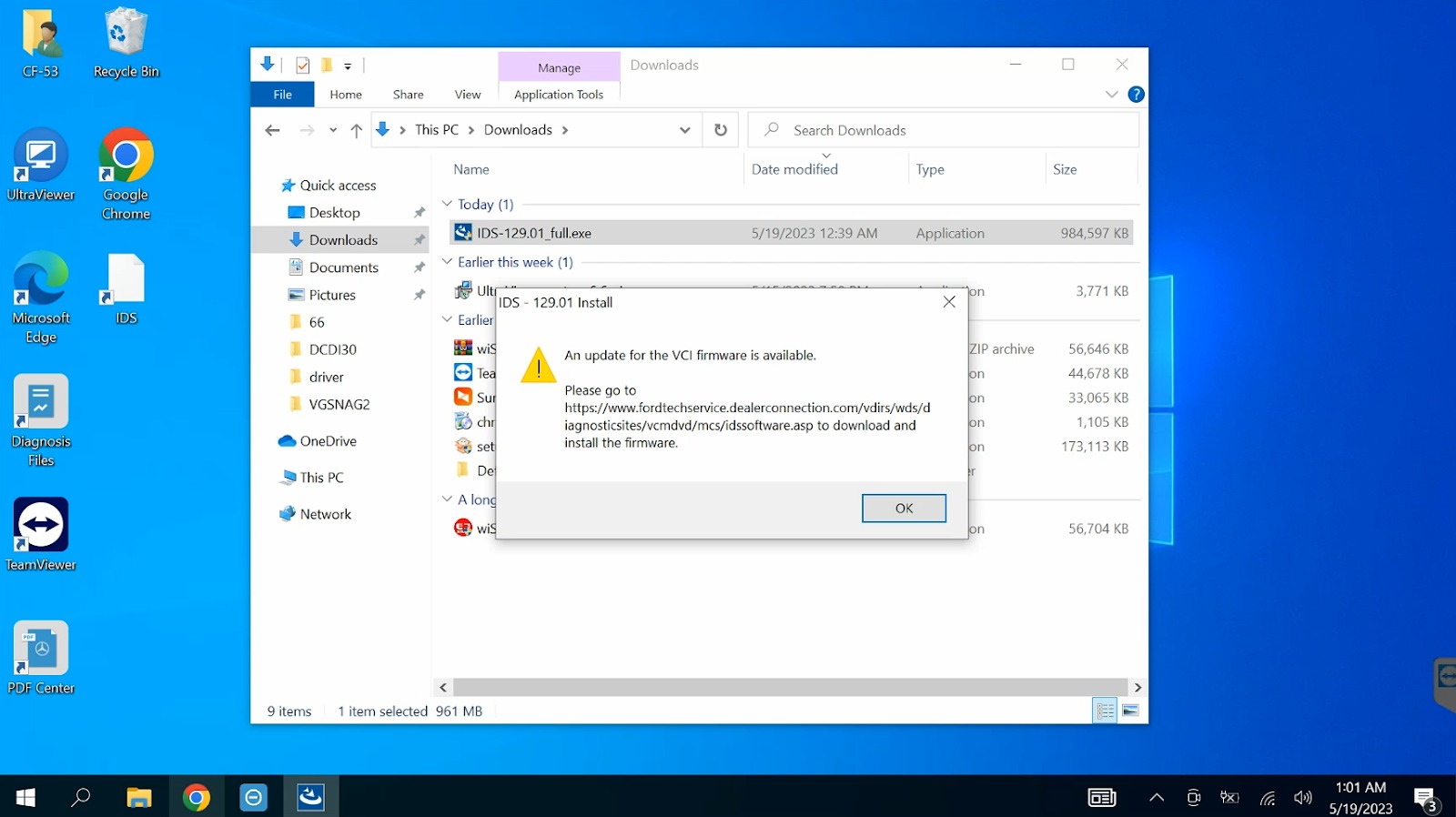
Select OK to continue installation
Step 4: Install IDS 129.07 Update
- After installing IDS 130, continue by downloading IDS 129.07 Update
- Open the file, run “Run as Administrator”, and wait for the installation to complete
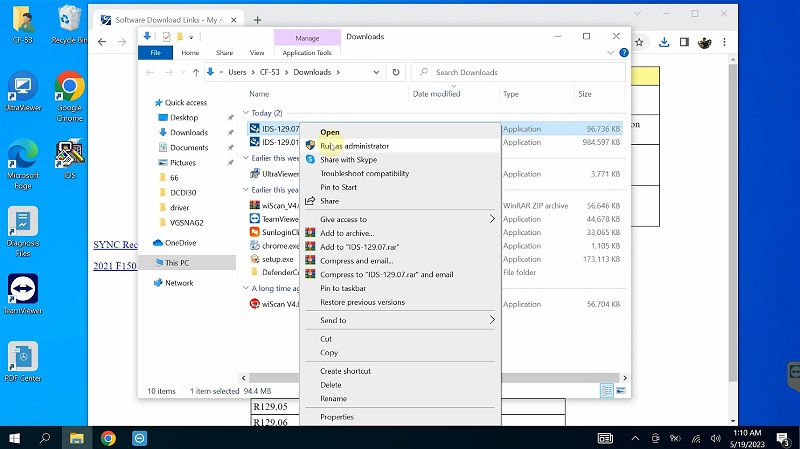
Launch the software by clicking “Run as administrators”
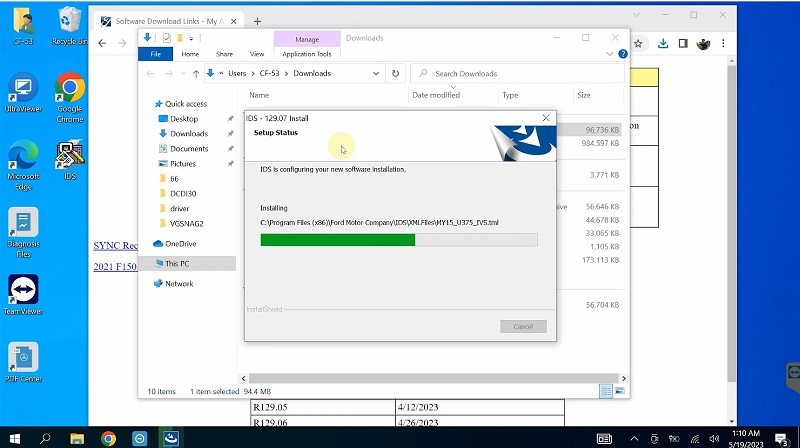
Waiting for Installing
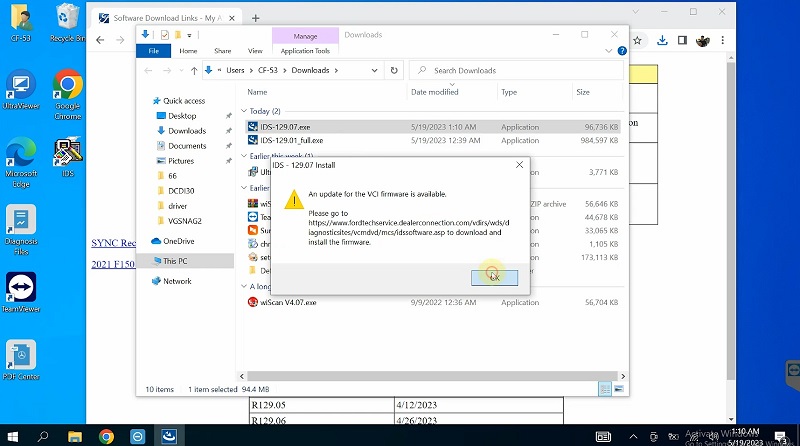
Press Next to continue
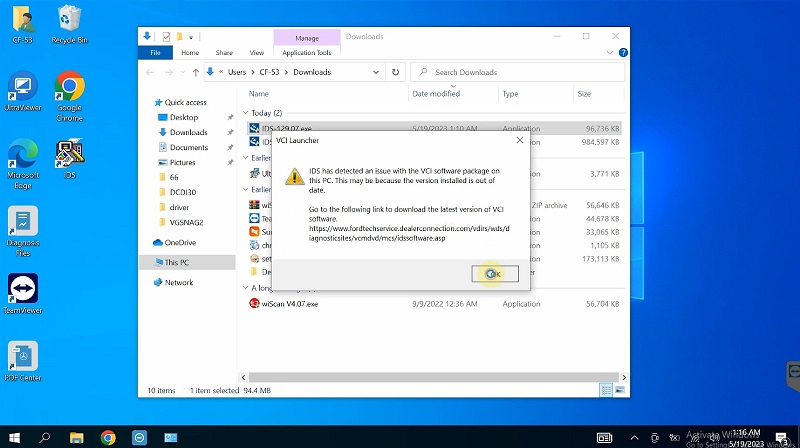
Click OK to complete
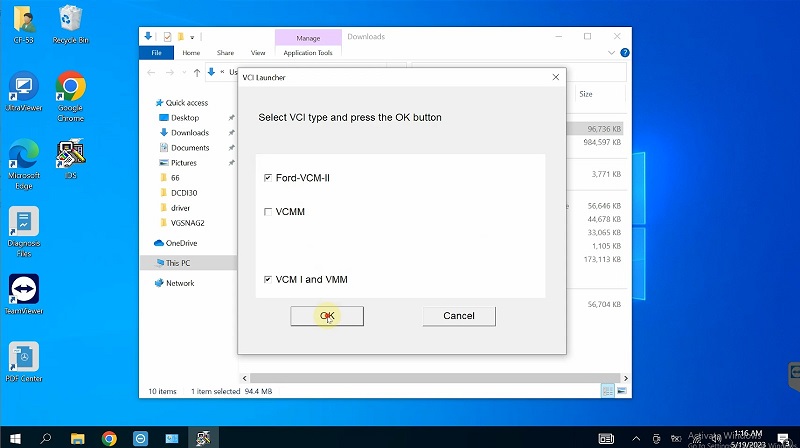
Select VCI type and press the OK button
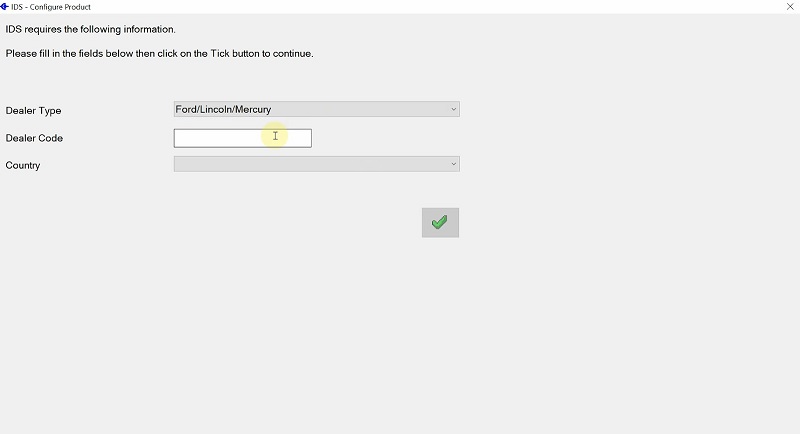
Fill the information
Step 5: Install Ford VCI Software
- Download and install Ford VCI Manager to enable connectivity with the VCM2 device
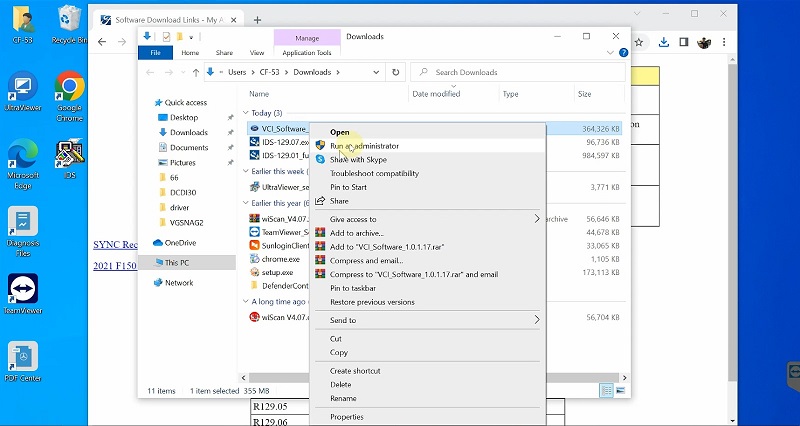
Run as Administrator
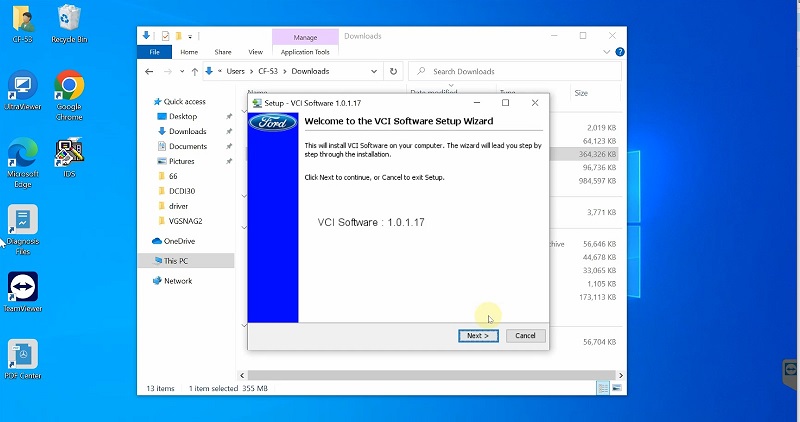
Click Next to Installing
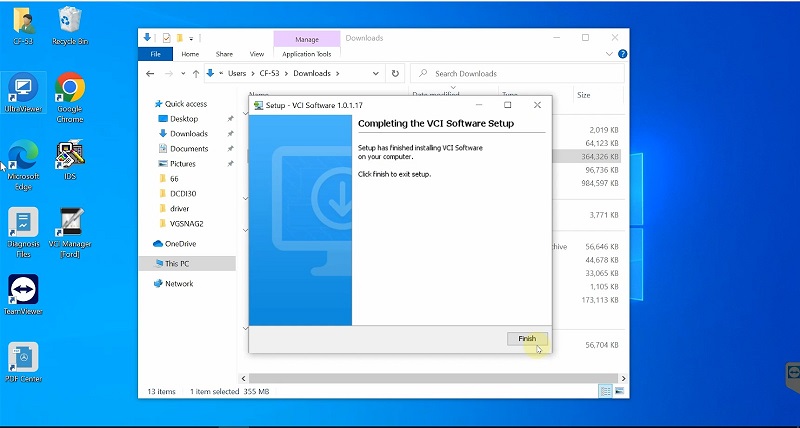
Click Finish
- Wait for the process to complete, then restart your computer

Interface IDS Software
Step 6: Connect VCM2 to the Computer and Ford Vehicle
- Plug the VCM2 device into the USB port on your computer
- Launch IDS Software and connect to your vehicle for diagnostics
Note: The IDS software will work without a license, but it cannot connect with your car. Before buying any hardware, you may examine the program interface and the various IDS functionalities by downloading the software.
Above are detailed instructions for downloading and installing IDS Software when you purchase products at VCCarTool. If you have any questions or difficulties while using the software, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for free consultation.
Video tutorial to download Ford IDS software:
3. Important Notes for a Successful Ford IDS Installation
- Ford IDS can be downloaded for free without a Ford FDRS license, but you cannot connect to a vehicle unless activated.
- Disable antivirus and firewall software to prevent installation blocks.
- Ensure your computer meets the system requirements to avoid crashes during installation.
- Do not let your computer go into sleep mode or shut down the screen while downloading and installing IDS.
Ford IDS User Guide – How to Use the Software
- Run IDS software as Administrator – it will auto-detect the vehicle.
- Start a new session and select “All other.”
- Connect to the PCM module and confirm using the green check mark.
- Check vehicle specifications and navigate to Self-Test.
- Select ‘All DTCs’ and read fault codes.
- Clear fault codes – system will recheck for remaining errors.
- Go to Data Logger to access detailed error data.
- Select error details, highlight the bold part, and activate the test.
- Confirm activation – your vehicle is now diagnosed and error-free!
If you encounter any issues while installing or using Ford IDS software, don’t hesitate to contact VCCarTool!
- WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927
- Email: [email protected]
- Website: vccartool
Let’s take a look at some of Ford’s diagnostic software and equipment:
- Ford PTS Login Dealerconnection Training Online
- VCM II Professional Diagnostic Tool for Ford
- FORD FJDS Software Activation Key Remote Install V130.9
