P0173 Code Mercedes: Fuel Trim, Causes, and How to Fix
The P0173 code Mercedes indicates a “Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank 2),” suggesting that the engine’s air-fuel mixture is not within the ideal range. This article explores the common causes of this diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and provides actionable steps for diagnosis and repair, ensuring optimal engine performance, reducing emissions, and preventing potential damage to your vehicle, let VCCarTool assist you with professional diagnostic support. Discover effective solutions now.
If you’re unsure about how to repair, diagnose, or program the P0173 code Mercedes, contact VCCarTool via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for assistance to avoid causing more severe errors.
1. Understanding the P0173 Code Mercedes
The P0173 code indicates that the Engine Control Unit (ECU) has detected an issue with the fuel trim on Bank 2 of your Mercedes-Benz engine. Fuel trim refers to the ECU’s ability to make minor adjustments to the air-fuel mixture to maintain optimal combustion. According to a study by the SAE International Journal of Engines, proper fuel trim is essential for minimizing emissions and maximizing fuel efficiency. When the P0173 code appears, it signals that the ECU has reached its limit in correcting the fuel mixture, indicating an underlying problem that needs to be addressed. The P0173 error code can trigger the check engine light and result in poor engine performance, decreased fuel economy, and possibly higher emissions. It’s important to diagnose and address this issue promptly.
1.1. What Does Fuel Trim Mean?
Fuel trim is the ECU’s method of fine-tuning the air-fuel mixture to maintain the ideal stoichiometric ratio of 14.7:1 (air to fuel). This ratio ensures efficient combustion, reduces harmful emissions, and optimizes engine performance. Fuel trim values are expressed as percentages; positive values indicate that the ECU is adding fuel to compensate for a lean condition (too much air), while negative values indicate that the ECU is reducing fuel to compensate for a rich condition (too much fuel).
1.2. Short-Term Fuel Trim (STFT) vs. Long-Term Fuel Trim (LTFT)
- Short-Term Fuel Trim (STFT): STFT values react quickly to changes in the air-fuel mixture. They are temporary adjustments made by the ECU in response to real-time sensor data. STFT values fluctuate rapidly and are used for immediate corrections.
- Long-Term Fuel Trim (LTFT): LTFT values are learned adjustments that the ECU stores over time. They represent more permanent corrections to the fuel mixture based on the average of the STFT values. LTFT values adjust more slowly than STFT and are used to compensate for long-term changes in engine conditions.
1.3. Bank 1 vs. Bank 2
In engines with more than one cylinder head (such as V6, V8, or V-shaped engines), each cylinder head is referred to as a “bank.” Bank 1 is the side of the engine that contains cylinder number one, while Bank 2 is the opposite side. The P0173 code specifically relates to fuel trim issues on Bank 2.
2. Common Symptoms of the P0173 Code Mercedes
Recognizing the symptoms associated with the P0173 code can help you diagnose the issue promptly and prevent further damage. Here are some common symptoms:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard.
- Poor Engine Performance: The engine may run rough, hesitate during acceleration, or lack power.
- Decreased Fuel Economy: You may notice a significant drop in your vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle roughly or stall, especially when cold.
- Increased Emissions: Your vehicle may fail an emissions test due to the improper air-fuel mixture.
3. Potential Causes of the P0173 Code Mercedes
Several factors can trigger the P0173 code in your Mercedes-Benz. Identifying the root cause is essential for an effective repair. Here are the most common culprits:
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks allow unmetered air to enter the engine, causing a lean condition. Common sources include cracked hoses, faulty intake manifold gaskets, and defective PCV valves.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Issues: The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A faulty MAF sensor can provide incorrect readings, leading to improper fuel trim adjustments.
- Oxygen (O2) Sensor Problems: O2 sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. If the O2 sensor on Bank 2 is malfunctioning, it can send incorrect data to the ECU, resulting in fuel trim errors.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors can disrupt the fuel supply to the cylinders on Bank 2, causing a lean or rich condition.
- Fuel Pump Issues: A weak or failing fuel pump may not deliver enough fuel to the engine, leading to a lean condition and triggering the P0173 code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Exhaust leaks before the O2 sensor can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream, affecting the O2 sensor’s readings and causing fuel trim problems.
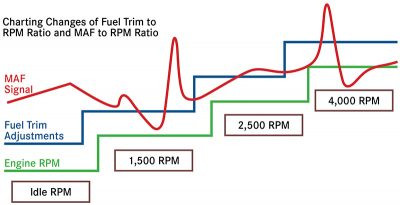 Fuel trim moving in step with RPM increases while MAF faulting
Fuel trim moving in step with RPM increases while MAF faulting
4. Diagnosing the P0173 Code Mercedes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing the P0173 code requires a systematic approach to identify the underlying issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you diagnose the problem:
4.1. Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use an OBD-II scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes stored in the ECU. Record all codes, including any related to fuel trim, O2 sensors, or MAF sensors. Clear the codes and take the vehicle for a test drive to see if the P0173 code returns.
4.2. Inspect for Vacuum Leaks
- Visual Inspection: Check all vacuum hoses, intake manifold gaskets, and PCV valves for cracks, leaks, or damage.
- Smoke Test: Use a smoke machine to introduce smoke into the intake system and identify any leaks. Smoke will escape from any points where there is a vacuum leak.
- Listen for Hissing Sounds: With the engine running, listen for hissing sounds that may indicate a vacuum leak.
4.3. Evaluate the MAF Sensor
- Visual Inspection: Check the MAF sensor for any visible damage or contamination.
- Live Data: Use an OBD-II scanner to monitor the MAF sensor’s readings while the engine is running. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. The MAF sensor should show a smooth and steady increase in airflow as the engine RPM increases.
- MAF Sensor Cleaning: If the MAF sensor appears dirty, carefully clean it with a MAF sensor cleaner. Reinstall the sensor and recheck the readings.
- MAF Sensor Testing: Use a multimeter to test the MAF sensor’s voltage and frequency according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.4. Assess the O2 Sensors
- Visual Inspection: Check the O2 sensors on Bank 2 for any visible damage or contamination.
- Live Data: Use an OBD-II scanner to monitor the O2 sensor’s readings while the engine is running. The O2 sensor should switch between rich and lean conditions, indicating that it is functioning properly.
- O2 Sensor Testing: Use a multimeter to test the O2 sensor’s voltage according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.5. Check Fuel Injectors
- Visual Inspection: Check the fuel injectors on Bank 2 for any visible damage or leaks.
- Fuel Injector Testing: Use a multimeter to test the fuel injectors’ resistance according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Fuel Injector Cleaning: If the fuel injectors are suspected to be clogged, have them professionally cleaned or replace them.
4.6. Examine Fuel Pressure
- Fuel Pressure Test: Use a fuel pressure gauge to measure the fuel pressure at the fuel rail. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Fuel Pump Inspection: If the fuel pressure is low, inspect the fuel pump for any signs of damage or wear.
4.7. Inspect for Exhaust Leaks
- Visual Inspection: Check the exhaust manifold, exhaust pipes, and gaskets for any signs of leaks, such as soot or corrosion.
- Listen for Exhaust Noises: With the engine running, listen for unusual exhaust noises that may indicate a leak.
If you encounter any issues during the diagnostic process or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to contact VCCarTool via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for expert guidance.
5. Repairing the P0173 Code Mercedes: Solutions and Steps
Once you have identified the root cause of the P0173 code, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are some common solutions and steps to fix the issue:
- Repair Vacuum Leaks:
- Replace any cracked or damaged vacuum hoses.
- Replace faulty intake manifold gaskets.
- Replace defective PCV valves.
- Replace the MAF Sensor:
- If the MAF sensor is faulty, replace it with a new, OEM-quality sensor.
- Ensure the new MAF sensor is properly installed and connected.
- Replace the O2 Sensor:
- If the O2 sensor on Bank 2 is malfunctioning, replace it with a new, OEM-quality sensor.
- Ensure the new O2 sensor is properly installed and connected.
- Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors:
- If the fuel injectors on Bank 2 are clogged or malfunctioning, have them professionally cleaned or replace them with new ones.
- Ensure the fuel injectors are properly installed and connected.
- Replace the Fuel Pump:
- If the fuel pump is weak or failing, replace it with a new, OEM-quality fuel pump.
- Ensure the new fuel pump is properly installed and connected.
- Repair Exhaust Leaks:
- Repair any exhaust leaks by welding or replacing damaged components.
- Replace any faulty exhaust gaskets.
5.1. Step-by-Step Repair Guide
- Gather Tools and Materials: Collect all the necessary tools, parts, and materials for the repair.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical damage.
- Perform the Repair: Follow the specific steps for the repair based on the identified cause.
- Reassemble Components: Carefully reassemble all components, ensuring they are properly connected and secured.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clear DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear the diagnostic trouble codes from the ECU.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the P0173 code does not return and that the engine is running smoothly.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the engine’s performance and fuel economy to ensure the issue is resolved.
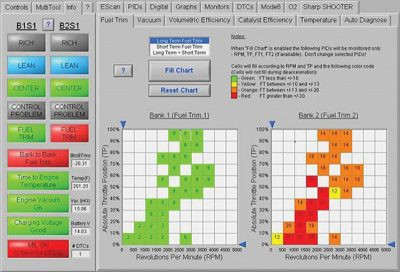 The Total Fuel Trim test in the Escan tool shows detail on each fuel trim adjustment throughout the RPM and load range on each bank
The Total Fuel Trim test in the Escan tool shows detail on each fuel trim adjustment throughout the RPM and load range on each bank
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for P0173
For complex cases or when the initial diagnostic steps do not resolve the issue, consider these advanced diagnostic techniques:
- Fuel Trim Reset: Reset the fuel trim values in the ECU to clear any learned adjustments that may be causing the problem.
- Data Logging: Use an advanced OBD-II scanner to log live data from the engine’s sensors while driving. Analyze the data to identify any anomalies or patterns that may be contributing to the P0173 code.
- Professional Diagnostic Services: Consult a professional mechanic or diagnostic specialist for expert assistance. They have specialized tools and knowledge to diagnose and repair complex issues. VCCarTool offers professional diagnostic services to help you resolve the P0173 code quickly and effectively. Contact us via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for more information.
7. Avoiding Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary repairs and expenses. Here are some tips to avoid misdiagnosing the P0173 code:
- Follow a Systematic Approach: Use a step-by-step diagnostic process to identify the root cause accurately.
- Verify Sensor Readings: Compare sensor readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure they are within the correct range.
- Check for Related Symptoms: Consider any related symptoms, such as rough idle or poor fuel economy, to help narrow down the potential causes.
- Consult Technical Resources: Refer to technical service bulletins (TSBs), repair manuals, and online forums for additional information and insights.
8. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid P0173 Code
Preventive maintenance can help you avoid the P0173 code and keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Here are some preventive measures:
- Regularly Inspect Vacuum Hoses: Check vacuum hoses for cracks, leaks, or damage and replace them as needed.
- Clean the MAF Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor every 30,000 miles to ensure accurate readings.
- Replace O2 Sensors: Replace O2 sensors every 60,000 to 100,000 miles to maintain optimal performance.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Use high-quality fuel to prevent fuel injector clogging and maintain fuel system performance.
- Perform Regular Engine Tune-Ups: Perform regular engine tune-ups, including spark plug replacement and air filter replacement, to ensure optimal engine performance.
9. Cost of Repairing the P0173 Code
The cost of repairing the P0173 code can vary depending on the underlying cause and the extent of the repairs needed. Here are some estimated costs for common repairs:
| Repair | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Leak Repair | $100 – $300 |
| MAF Sensor Replacement | $200 – $400 |
| O2 Sensor Replacement | $150 – $350 |
| Fuel Injector Cleaning | $100 – $250 |
| Fuel Pump Replacement | $300 – $600 |
| Exhaust Leak Repair | $150 – $400 |
Note: These costs are estimates and may vary depending on your location, the specific make and model of your vehicle, and the repair shop you choose.
10. Advantages of Using VCCarTool for Diagnostic Support
When dealing with complex issues like the P0173 code, having expert support can make all the difference. VCCarTool offers several advantages:
- Expert Guidance: Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert guidance and support throughout the diagnostic and repair process.
- Remote Diagnostics: We offer remote diagnostic services to help you identify the root cause of the P0173 code quickly and accurately.
- Customized Solutions: We provide customized solutions tailored to your specific vehicle and situation.
- Cost-Effective: Our services are cost-effective, helping you save time and money on unnecessary repairs.
Don’t let the P0173 code affect your vehicle’s performance. Contact VCCarTool via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 today for expert diagnostic support and get your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly again.
11. Conclusion
The P0173 code Mercedes indicates a fuel trim malfunction on Bank 2, which can lead to various performance issues. By understanding the potential causes, following a systematic diagnostic approach, and performing the necessary repairs, you can resolve the P0173 code and restore your vehicle’s optimal performance. Remember to consider advanced diagnostic techniques and preventive maintenance to avoid future issues. If you need expert assistance, VCCarTool is here to help.
12. FAQ About P0173 Code Mercedes
-
What does the P0173 code mean on a Mercedes-Benz?
The P0173 code indicates a “Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank 2)” in your Mercedes-Benz, signaling that the engine’s air-fuel mixture is not within the ideal range. -
Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the P0173 code?
While it’s possible to drive with the P0173 code, it’s not recommended. The underlying issue can cause poor engine performance, decreased fuel economy, and potential damage to your vehicle. -
What are the common causes of the P0173 code?
Common causes include vacuum leaks, a faulty MAF sensor, O2 sensor problems, fuel injector issues, and exhaust leaks. -
How do I diagnose the P0173 code?
Diagnose the P0173 code by scanning for DTCs, inspecting for vacuum leaks, evaluating the MAF and O2 sensors, checking fuel injectors, and examining fuel pressure. -
Can a dirty MAF sensor cause the P0173 code?
Yes, a dirty or faulty MAF sensor can provide incorrect readings, leading to improper fuel trim adjustments and triggering the P0173 code. -
How do I fix a vacuum leak on my Mercedes-Benz?
Fix vacuum leaks by replacing cracked hoses, faulty intake manifold gaskets, or defective PCV valves. -
What is the role of O2 sensors in fuel trim?
O2 sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. If they malfunction, they can send incorrect data to the ECU, resulting in fuel trim errors. -
How often should I replace my O2 sensors?
Replace O2 sensors every 60,000 to 100,000 miles to maintain optimal performance. -
Can VCCarTool help me diagnose and repair the P0173 code?
Yes, VCCarTool offers expert diagnostic support and customized solutions to help you resolve the P0173 code quickly and effectively. Contact us via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for more information. -
What is the estimated cost to repair the P0173 code?
The cost can vary, but common repairs range from $100 for vacuum leak repairs to $600 for fuel pump replacement, depending on the cause and extent of the repair.
Are you struggling with the P0173 code on your Mercedes-Benz? Don’t waste time and money on guesswork. Contact VCCarTool today for expert diagnostic support and customized solutions. Our team of experienced technicians is ready to help you identify the root cause of the issue and get your vehicle running smoothly again. Reach out to us via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927, email at [email protected], or visit our website at vccartool.com for more information. Let VCCarTool be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair.
