EEPROM vs Flash Memory: What’s the Difference & Which Is Best?
Are you confused about EEPROM vs flash memory and which one suits your automotive repair needs? VCCarTool clarifies the differences in this comprehensive guide, helping you make the best choice for your diagnostic and programming tasks. Discover the key factors, from write speeds to storage capacity, and empower your repair shop with the right technology. Enhance your diagnostic capabilities today with VCCarTool and our expert support via WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927. Master memory solutions with confidence.
1. Understanding the Basics of EEPROM
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. This technology is commonly used in various electronic devices for storing relatively small amounts of data that need to be updated occasionally.
1.1. Key Features of EEPROM
- Byte-Level Alterability: Unlike some other types of memory, EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed at the byte level, offering precise control over data modification.
- Non-Volatile Storage: EEPROM retains stored data even when power is removed, making it ideal for storing configuration settings and calibration data in automotive systems.
- Limited Write Cycles: EEPROM has a limited number of write/erase cycles compared to other memory types like flash memory.
1.2. How EEPROM Works
EEPROM cells typically use a floating-gate transistor. Writing data involves applying a voltage to the gate to trap electrons, changing the cell’s state. Erasing data involves removing the trapped electrons, which also requires a voltage. This process can be done electrically, making it convenient for in-system updates.
1.3. Common Applications of EEPROM in Automotive Repair
- Storing Configuration Settings: EEPROM is used to store vehicle configuration settings, such as radio presets, seat positions, and mirror adjustments.
- Calibration Data: It stores calibration data for sensors and actuators, ensuring accurate performance.
- Firmware Storage: In some cases, EEPROM holds firmware code for microcontrollers within automotive ECUs (Electronic Control Units).
2. Delving into Flash Memory Technology
Flash memory is another type of non-volatile memory that offers high storage capacity and fast read speeds. It is widely used in devices like USB drives, SSDs (Solid State Drives), and memory cards. In automotive applications, flash memory plays a crucial role in storing large amounts of data such as maps, multimedia content, and software updates.
2.1. Key Features of Flash Memory
- High Storage Capacity: Flash memory offers significantly higher storage capacity compared to EEPROM, making it suitable for storing large files and data sets.
- Fast Read Speeds: Flash memory provides fast read speeds, enabling quick access to stored data.
- Block-Level Operations: Flash memory operates on blocks of data, meaning that data is erased and written in blocks rather than individual bytes.
2.2. How Flash Memory Operates
Flash memory also uses floating-gate transistors to store data. Writing data involves injecting electrons into the floating gate, while erasing data involves removing electrons. However, unlike EEPROM, flash memory must erase an entire block of data before writing new data.
2.3. Automotive Uses of Flash Memory
- Navigation Systems: Flash memory stores map data for navigation systems, allowing drivers to access real-time directions.
- Infotainment Systems: It stores multimedia content such as music, videos, and images for infotainment systems.
- ECU Firmware: Flash memory stores the main firmware code for ECUs, enabling software updates and feature enhancements.
 Flash Memory for automotive uses
Flash Memory for automotive uses
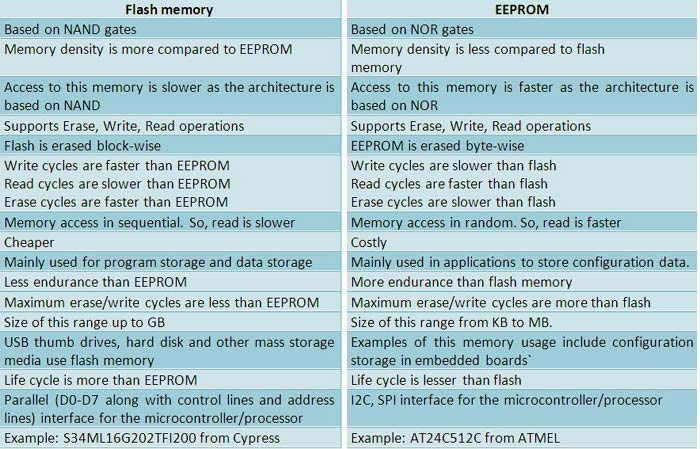
3. EEPROM vs Flash: Key Differences Highlighted
When considering EEPROM vs flash memory, understanding the fundamental differences is crucial for making informed decisions. Here’s a comprehensive comparison to guide you.
3.1. Operational Differences
| Feature | EEPROM | Flash Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Write/Erase | Byte-level | Block-level |
| Speed | Faster at byte level | Slower due to block operations |
| Density | Lower | Higher |
| Endurance | Limited write cycles | Better endurance with wear-leveling |
| Data Retention | Good | Good, often better due to wear-leveling |
| Power Consumption | Generally lower for small operations | Can be higher during block erase/write cycles |
3.2. Performance Metrics
EEPROM excels in applications requiring frequent, small data updates because of its byte-level alterability. Flash memory is better for storing large volumes of data where updates are less frequent due to its block-level operations, which can be slower.
3.3. Cost and Capacity
- Cost: EEPROM is generally more expensive per bit of storage compared to flash memory.
- Capacity: Flash memory offers significantly higher storage capacities, making it more cost-effective for large storage needs.
3.4. Endurance and Reliability
Flash memory often employs wear-leveling techniques to extend its lifespan by evenly distributing write/erase cycles across the memory array. This makes it more durable for applications involving frequent data updates.
3.5. Interface and Integration
- EEPROM: Typically uses serial interfaces like I2C or SPI.
- Flash Memory: Often uses parallel interfaces for faster data transfer.
3.6. Real-World Applications
EEPROM is used in automotive systems for storing configuration settings, calibration data, and small firmware updates. Flash memory is used in navigation systems, infotainment systems, and storing ECU firmware.
If you’re unsure which memory type suits your needs, contact VCCarTool for expert guidance. Our team can help you choose the right solution and provide support for your automotive repair tasks. Reach out to us on WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for immediate assistance.
4. Which One to Choose: Matching Memory to Task
Selecting between EEPROM vs flash memory involves assessing the unique requirements of your application. Here’s a guide to help you make the right decision.
4.1. Scenarios Favoring EEPROM
- Frequent Small Data Updates: EEPROM is ideal when you need to update small amounts of data frequently, such as configuration settings or calibration parameters.
- Low Storage Requirements: If your storage needs are relatively small, EEPROM can provide a cost-effective solution.
- Byte-Level Control: When you need precise control over individual bytes of data, EEPROM’s byte-level alterability is advantageous.
4.2. Situations Where Flash Memory Excels
- Large Data Storage: Flash memory is the preferred choice when you need to store large amounts of data, such as maps, multimedia files, or firmware code.
- Fast Read Speeds: If your application requires fast read speeds, flash memory can provide quick access to stored data.
- Infrequent Updates: Flash memory is suitable for applications where data updates are less frequent, such as storing ECU firmware that is updated periodically.
4.3. Automotive Diagnostic Tools and Memory Choices
In automotive diagnostic tools, EEPROM might be used for storing tool configuration settings, while flash memory could store diagnostic software and vehicle data.
4.4. Programming and ECU Tuning Considerations
When programming or tuning ECUs, the choice between EEPROM vs flash memory depends on the specific requirements of the task. EEPROM may be used for storing calibration data, while flash memory is used for storing the main ECU firmware.
5. Practical Examples in Automotive Repair
Understanding how EEPROM vs flash memory are used in real-world automotive repair scenarios can provide valuable insights. Here are some practical examples to illustrate their applications.
5.1. Storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
EEPROM can be used to store DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) in the vehicle’s ECU. This allows technicians to retrieve and analyze fault codes to diagnose issues with the vehicle.
5.2. Saving Vehicle Configuration Settings
EEPROM is commonly used to store vehicle configuration settings, such as radio presets, seat positions, and mirror adjustments. This ensures that these settings are retained even when the vehicle’s battery is disconnected.
5.3. Updating ECU Firmware
Flash memory is used to store the main firmware code for ECUs. This allows manufacturers to release software updates and feature enhancements that can be installed on the vehicle.
5.4. Storing Map Data for Navigation Systems
Flash memory stores map data for navigation systems, providing drivers with real-time directions and points of interest.
5.5. Managing Multimedia Content in Infotainment Systems
Flash memory stores multimedia content such as music, videos, and images for infotainment systems, providing entertainment options for drivers and passengers.
6. How VCCarTool Can Help You Navigate Memory Choices
VCCarTool offers a range of diagnostic and programming tools that can help you navigate the complexities of EEPROM vs flash memory. Our tools are designed to support various automotive repair tasks, from reading and writing EEPROM data to flashing ECU firmware.
6.1. Diagnostic Tools Supporting EEPROM and Flash
Our diagnostic tools support both EEPROM and flash memory, allowing you to read and write data from various vehicle modules.
6.2. Programming Solutions for ECU Tuning
VCCarTool provides programming solutions for ECU tuning, allowing you to modify calibration data and update firmware code.
6.3. Expert Support and Guidance
Our team of experts can provide support and guidance to help you choose the right memory solution for your needs. Contact us on WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for immediate assistance.
6.4. Training Resources and Tutorials
VCCarTool offers training resources and tutorials to help you learn more about EEPROM vs flash memory and how to use our tools effectively.
7. Step-by-Step Guide: Working with EEPROM and Flash
Working with EEPROM and flash memory requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you perform common tasks.
7.1. Reading EEPROM Data
- Connect your diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Select the appropriate module to read EEPROM data from.
- Follow the tool’s instructions to read and save the EEPROM data.
7.2. Writing EEPROM Data
- Connect your programming tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Select the appropriate module to write EEPROM data to.
- Load the EEPROM data file that you want to write.
- Follow the tool’s instructions to write the EEPROM data.
7.3. Flashing ECU Firmware
- Connect your programming tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Select the appropriate ECU to flash.
- Load the firmware file that you want to flash.
- Follow the tool’s instructions to flash the ECU firmware.
7.4. Best Practices for Data Handling
- Always back up your data before making any changes.
- Use reliable tools and software.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- Ensure a stable power supply during programming operations.
 Flash Memory for automotive uses
Flash Memory for automotive uses
8. The Future of Automotive Memory Technology
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and memory technology is no exception. Here’s a glimpse into the future of EEPROM vs flash memory in automotive applications.
8.1. Emerging Memory Technologies
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express): Offers faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to traditional flash memory.
- ReRAM (Resistive Random-Access Memory): Provides high storage density, low power consumption, and fast write speeds.
- MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random-Access Memory): Offers non-volatility, high speed, and high endurance.
8.2. Trends in Automotive Memory Usage
- Increasing Storage Capacity: As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the need for storage capacity will continue to grow.
- Faster Data Transfer Speeds: Faster data transfer speeds will be essential for real-time processing of sensor data and decision-making.
- Enhanced Security Features: Memory devices will need to incorporate enhanced security features to protect against cyber threats.
8.3. VCCarTool’s Vision for Innovation
VCCarTool is committed to staying at the forefront of automotive memory technology. We continuously invest in research and development to bring you the latest and most innovative tools and solutions.
9. Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions surrounding EEPROM vs flash memory. Let’s address some of the most common ones.
9.1. “Flash Memory is Always Better than EEPROM”
While flash memory offers higher storage capacity and faster read speeds, EEPROM is still valuable for applications requiring frequent small data updates.
9.2. “EEPROM is Outdated Technology”
EEPROM remains relevant for specific applications where its byte-level alterability is advantageous.
9.3. “All Flash Memory is the Same”
There are different types of flash memory, such as NAND and NOR, each with its own characteristics and applications.
9.4. “You Can’t Trust Aftermarket Memory Solutions”
While it’s essential to choose reliable memory solutions, many aftermarket options offer excellent performance and reliability. VCCarTool provides high-quality, trustworthy memory solutions for your automotive repair needs.
10. FAQs: Your Burning Questions Answered
10.1. What is the main difference between EEPROM and Flash memory?
EEPROM allows byte-level writes and erases, while flash memory requires block-level erasing before writing.
10.2. Which one is faster, EEPROM or Flash memory?
EEPROM is faster for byte-level operations, while flash memory can offer faster read speeds for large data blocks.
10.3. Which one has a longer lifespan, EEPROM or Flash memory?
Flash memory typically has a longer lifespan due to wear-leveling techniques.
10.4. Can I use Flash memory to replace EEPROM in all applications?
No, EEPROM is still preferred for applications requiring frequent small data updates.
10.5. What are the common applications of EEPROM in automotive repair?
EEPROM is used for storing configuration settings, calibration data, and DTCs.
10.6. What are the common applications of Flash memory in automotive repair?
Flash memory is used for storing map data, multimedia content, and ECU firmware.
10.7. How can VCCarTool help me choose between EEPROM and Flash memory?
VCCarTool offers expert support and diagnostic tools to help you choose the right memory solution. Contact us on WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927 for assistance.
10.8. Are there any risks involved in working with EEPROM and Flash memory?
Yes, there are risks such as data corruption and ECU damage if not handled properly. Always follow best practices and use reliable tools.
10.9. How do wear-leveling algorithms work in Flash memory?
Wear-leveling algorithms distribute write/erase cycles evenly across the memory array to prevent specific blocks from wearing out prematurely.
10.10. What are the emerging memory technologies in the automotive industry?
Emerging technologies include NVMe, ReRAM, and MRAM, which offer faster speeds, higher density, and enhanced security features.
11. Conclusion: Empowering Your Automotive Repair with the Right Memory Choice
Choosing between EEPROM vs flash memory is critical for optimizing your automotive repair tasks. EEPROM offers byte-level precision for settings and calibrations, while flash memory provides high capacity for maps and firmware.
VCCarTool provides the tools, support, and expertise you need to make informed decisions and enhance your repair capabilities. Whether you’re diagnosing issues, tuning ECUs, or updating firmware, we have the right solution for you.
Ready to enhance your automotive repair capabilities? Contact VCCarTool today for expert guidance and solutions tailored to your needs. Reach out to us on WhatsApp: +1 (901) 414 – 1927, email us at [email protected], or visit our website at vccartool.com. Let us help you drive your business forward.
